Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Services is a popular desktop virtualization product. RDS provides users with a Windows client desktop that is shared among other users on Windows Server and allows administrators to provide a Windows desktop experience for many users at once, using one or more servers and a Remote Desktop Protocol client.
As such, RDS is a valuable and widely available tool for operations continuity, empowering workers with the capabilities to function both in the office and away from it.
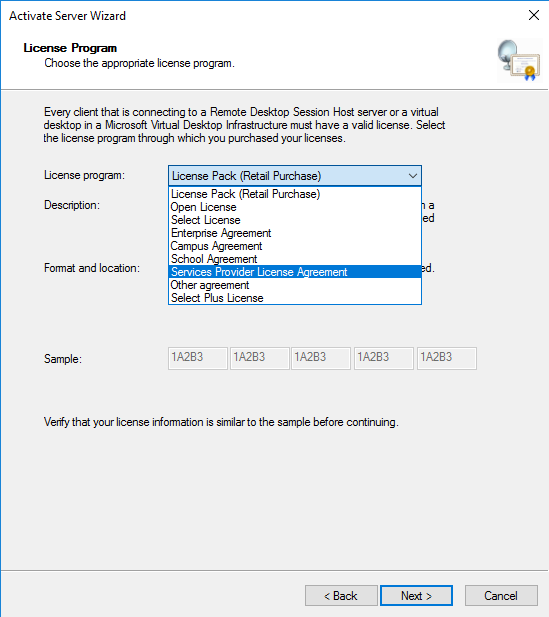
With two servers, administrators can set up an entire RDS implementation in only four steps.
1. Install RDS Base Roles
In Remote Desktop Connection, type the name of the PC you want to connect to (from Step 1), and then select Connect. On your Windows, Android, or iOS device: Open the Remote Desktop app (available for free from Microsoft Store, Google Play, and the Mac App Store), and add the name of the PC that you want to connect to (from Step 1).
Each user and device that connects to a Remote Desktop Session host needs a client access license (CAL). You use RD Licensing to install, issue, and track RDS CALs. When a user or a device connects to an RD Session Host server, the RD Session Host server determines if an RDS CAL is needed. Original product version: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 Original KB number: 2833839. When you create a standard deployment of Remote Desktop Services, the Remote Desktop Connection Broker role service provides access to the complete functionality of Remote Desktop Services. . Starting with Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (1709), look for Remote Desktop under System in the Settings app instead of using the Remote Desktop Assistant. Microsoft Remote Desktop assistant allows you to configure your PC for remote access From your Windows PC, access the Microsoft Remote Desktop assistant to configure it for remote.
A typical RDS implementation has five roles: Remote Desktop Connection Broker, Remote Desktop Web Access, Remote Desktop Session Host, Remote Desktop Licensing and Remote Desktop Gateway.
Think of the RD Connection Broker, RD Web Access and the RD Session Host roles as base roles, which need to be installed on the primary RDS server.
Within the Add Roles and Features wizard, select Remote Desktop Services installation using the Quick Start option on Windows Server. The RDS wizard will then serve as a guide to installing all of these roles at once.
2. Install the Licensing Server

From within the Server Manager application, add a server to manage what will become a licensing server. Navigate to Remote Desktop Services and click on the green plus sign for RD Licensing. From there, add the other server on the Add RD Licensing Servers screen.
Once Windows installs the licensing server, a green plus sign should be visible above RD Licensing in the RDS Deployment Overview section.
3. Add RD Gateway Role
On the Remote Desktop Services screen, click on the green plus sign over RD Gateway, then select the destination server. When prompted, name the self-signed SSL certificate with a fully qualified domain and click Next to add the role.
4. Configure Deployment Properties
Once all roles are installed, navigate to the Remote Desktop Services screen, click on Tasks, then click on Edit Deployment Properties. On this screen, click on RD Licensing, choose Per User or Per Device settings depending on your agency’s needs and click OK. These settings will provide a basic RDS setup.

More On
Related Articles
-->Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016
Each user and device that connects to a Remote Desktop Session host needs a client access license (CAL). You use RD Licensing to install, issue, and track RDS CALs.
When a user or a device connects to an RD Session Host server, the RD Session Host server determines if an RDS CAL is needed. The RD Session Host server then requests an RDS CAL from the Remote Desktop license server. If an appropriate RDS CAL is available from a license server, the RDS CAL is issued to the client, and the client is able to connect to the RD Session Host server and from there to the desktop or apps they're trying to use.
There is a licensing grace period of 120 Days during which no license server is required. Once the grace period ends, clients must have a valid RDS CAL issued by a license server before they can log on to an RD Session Host server.
Use the following information to learn about how client access licensing works in Remote Desktop Services and to deploy and manage your licenses:
- License your RDS deployment with client access licenses (CALs)
Microsoft Remote Desktop Hostname
Understanding the RDS CAL model
There are two types of RDS CALs:
- RDS Per Device CALs
- RDS Per User CALs
The following table outlines the differences between the two types of CALs:
| Per Device | Per User |
|---|---|
| RDS CALs are physically assigned to each device. | RDS CALs are assigned to a user in Active Directory. |
| RDS CALs are tracked by the license server. | RDS CALs are tracked by the license server. |
| RDS CALs can be tracked regardless of Active Directory membership. | RDS CALs cannot be tracked within a workgroup. |
| You can revoke up to 20% of RDS CALs. | You cannot revoke any RDS CALs. |
| Temporary RDS CALs are valid for 52–89 days. | Temporary RDS CALs are not available. |
| RDS CALs cannot be overallocated. | RDS CALs can be overallocated (in breach of the Remote Desktop licensing agreement). |
When you use the Per Device model, a temporary license is issued the first time a device connects to the RD Session Host. The second time that device connects, as long as the license server is activated and there are available RDS CALs, the license server issues a permanent RDS Per Device CAL.
Borderlands 2: assassin supremacy pack download for mac. When you use the Per User model, licensing is not enforced and each user is granted a license to connect to an RD Session Host from any number of devices. The license server issues licenses from the available RDS CAL pool or the Over-Used RDS CAL pool. It's your responsibility to ensure that all of your users have a valid license and zero Over-Used CALs—otherwise, you're in violation of the Remote Desktop Services license terms.
An example of where one would use the Per Device model would be in an environment where there are two or more shifts using the same computers to access the RD Session Host(s). The Per User model would be best for environments where users have their own dedicated Windows device to access the RD Session Host(s).
To ensure you are in compliance with the Remote Desktop Services license terms, track the number of RDS Per User CALs used in your organization and be sure to have enough RDS Per User CALs installed on the license server for all of your users.
You can use the Remote Desktop Licensing Manager to track and generate reports on RDS Per User CALs.
RDS CAL version compatibility
The RDS CAL for your users or devices must be compatible with the version of Windows Server that the user or device is connecting to. You can't use RDS CALs for earlier versions to access later versions of Windows Server, but you can use later versions of RDS CALs to access earlier versions of Windows Server. For example, an RDS 2016 CAL or higher is required to connect to a Windows Server 2016 RD Session Host, while an RDS 2012 CAL or higher is required to connect to a Windows Server 2012 R2 RD Session Host.
The following table shows which RDS CAL and RD Session Host versions are compatible with each other.
Remote Desktop
| RDS 2008 R2 and earlier CAL | RDS 2012 CAL | RDS 2016 CAL | RDS 2019 CAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008, 2008 R2 session host | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2012 session host | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2012 R2 session host | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2016 session host | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 2019 session host | No | No | No | Yes |
You must install your RDS CAL on a compatible RD license server. Any RDS license server can host licenses from all previous versions of Remote Desktop Services and the current version of Remote Desktop Services. For example, a Windows Server 2016 RDS license server can host licenses from all previous versions of RDS, while a Windows Server 2012 R2 RDS license server can only host licenses up to Windows Server 2012 R2.
Download Remote Desktop Windows 10
The following table shows which RDS CAL and license server versions are compatible with each other.
| RDS 2008 R2 and earlier CAL | RDS 2012 CAL | RDS 2016 CAL | RDS 2019 CAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008, 2008 R2 license server | Yes | No | No | No |
| 2012 license server | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 2012 R2 license server | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 2016 license server | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| 2019 license server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
